What is it used for ?
There are very few indications for arthroscopy with osteoarthritis. However, it can be proposed with knee osteoarthritis when there is a suspected presence of a piece of cartilage in the joint or the meniscus is mobile and unstable.
How does it work ?
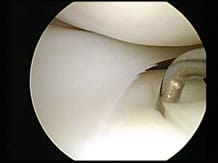
The procedure is carried out in an operating theatre and requires a short hospital stay (24 to 48 hours). It is performed under local, epidural or general anaesthetic. It involves introducing a tiny camera into the centre of the diseased joint to assess the damage caused by osteoarthritis.
It also enables “cleansing” the joint to rid it of cartilaginous or meniscal debris, either by carrying out a joint lavage or directly using forceps. Effectively, thanks to the two incisions made, the practitioner is able to introduce the necessary instruments into the area.
He or she can also normalise the joint surfaces.
What precautions need to be taken ?
It is advisable to rest the joint following the treatment.
Complications that may arise are those associated with the surgical procedure (anaesthesia complications, risk of phlebitis, pulmonary embolism) as well as those associated with surgery on a joint (infections, algodystrophy).